Let
![]() be a quadratic polynomial. We want to factor
be a quadratic polynomial. We want to factor
![]() over
over
![]() . First we test whether
. First we test whether ![]() is irreducible; if
so, we are done. Otherwise we know that
is irreducible; if
so, we are done. Otherwise we know that ![]() can be factored
as
can be factored
as
![]() where
where
![]() . We want to find
. We want to find ![]() and
and ![]() .
.
It suffices to find a polynomial that splits ![]() .
.
If ![]() then
then ![]() splits
splits ![]() . So if
. So if ![]() does not split
does not split ![]() then we know that
then we know that ![]() . We may also assume that
. We may also assume that ![]() (why?)
(why?)

We start with an easy case. Suppose
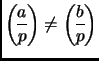 . In this case, according to the preceding
exercise,
. In this case, according to the preceding
exercise,
![]() splits
splits ![]() .
.
If now
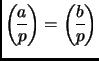 , our next trick is to
consider the polynomials
, our next trick is to
consider the polynomials
![]() . Ideally, we want to find
. Ideally, we want to find ![]() such
that
such
that
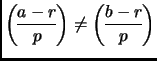 . Then
. Then
![]() splits
splits ![]() and therefore we can factor
and therefore we can factor ![]() . The next exercise
shows that we have an excellent chance of finding
. The next exercise
shows that we have an excellent chance of finding ![]() by just picking
it at random.
by just picking
it at random.
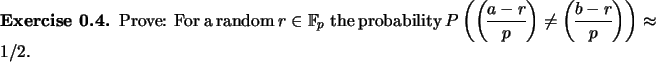
![]()