


Next: Isometries of Euclidean spaces
Up: Discrete Math, Third Problem
Previous: Linear algebra
Let
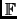 denote
denote
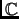 or
or
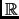 .
.
Definition 3.1
A bilinear map
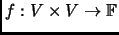
is a
Hermitian form if
Example 3.2
Define
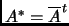
. A matrix
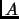
is
Hermitian if
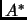
=
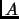
.
Given such a matrix, then
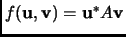
is a Hermitian form.
Exercise 3.3
Show that any Hermitian form can be written as above for some Hermitian matrix
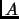
.
Definition 3.5
A
Euclidean space is a pair
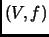
consisting of a vector space
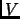
(over
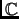
or
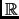
) and a positive definite Hermitian form
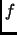
.
Example 3.6
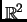
with the usual dot product
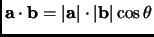
, where
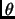
is the angle between
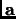
and
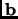
is an example; this is the same as
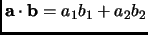
.
Definition 3.7
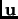
is
perpendicular to
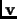
, denoted by
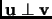
, if
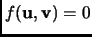
.
We define the
norm of
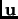
by
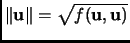
.
Definition 3.8
An
orthonormal basis is a basis
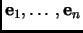
such that
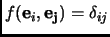
.
Theorem 3.9
Every finite-dimensional Euclidean space has an orthonormal basis.
Expressing a vector in coordinates involves solving an inhomogeneous system of equations. However if we wish to express
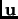 in orthonormal coordinates
in orthonormal coordinates
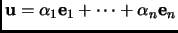
, we calculate
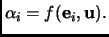



Next: Isometries of Euclidean spaces
Up: Discrete Math, Third Problem
Previous: Linear algebra
Varsha Dani
2003-07-25
![]() denote
denote
![]() or
or
![]() .
.
![]() in orthonormal coordinates
in orthonormal coordinates