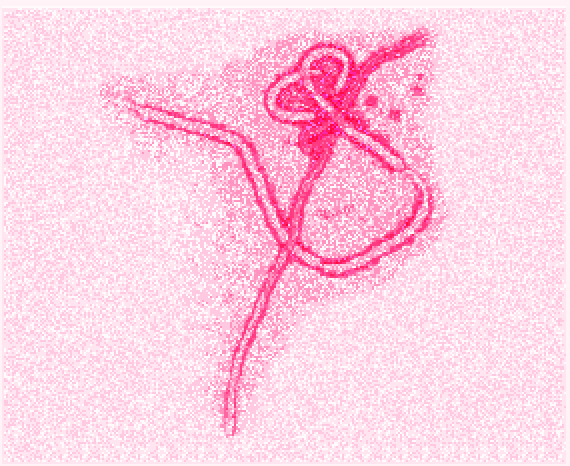Ebola is a member of the RNA virus family Filoviridae. These filoviruses (Ebola, Marburg and Reston) are very similar in morphology, density and sodium dodecyl sulfate - polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE) profile (Klenk, 1994). The particles are pleomorphic, meaning they can exist in many shapes.
Their basic structure is long and filamentious, essentially bacilliform, but the viruses often takes on a "U" shape, and the particles can be up to 14,000 nm in length and averagea 80 nm in diameter. The virus consists of a nucleocapsid, surrounded by a cross-striated helical capsid. There is an axial channel in the nucleocapsid, and the whole virion is surrounded by a lipoprotein unit derived from the host cell. In addition, there are 7 nm spikes placed 10 nm apart visible on the surface of the virion.