A histogram is a structure for representing a discrete approximation
of a probability distribution function. Given some variable ![]() , a
histogram of
, a
histogram of ![]() can be thought of as a series of ``bins'' which
collect occurrences of
can be thought of as a series of ``bins'' which
collect occurrences of ![]() based on the value
based on the value ![]() attains. The value
of the histogram at some bin is the number of occurrences of
attains. The value
of the histogram at some bin is the number of occurrences of ![]() (``hits'') in that bin. The usefulness of histograms is that they can
provide a compact summary of large amounts of data, in the sense that
statistical quantities (such as the mean or variance) which can be
measured directly from the data can often be measured more easily
from a histogram of that data.
(``hits'') in that bin. The usefulness of histograms is that they can
provide a compact summary of large amounts of data, in the sense that
statistical quantities (such as the mean or variance) which can be
measured directly from the data can often be measured more easily
from a histogram of that data.
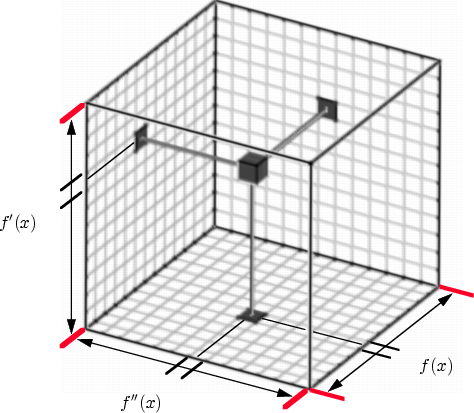
In our case, we have three variables, ![]() ,
, ![]() , and
, and ![]() , but we
want to do more than measure their individual probability
distributions. We are interested in the probabilities associated with
the relationship between the three variables. The most
straight-forward way to do this is with a three dimensional histogram,
with one axis for each of the variables. The span of each axis
represents a fixed range of values for the corresponding variable.
Each axis is divided into some number of (one dimensional) bins,
causing the interior volume is to be divided into a three dimensional
array of rectilinear bins, not unlike the voxels of a standard
volumetric dataset. Each bin in the three dimensional histogram
represents the combination of a small range of values in each of the
three variables. The value stored in each bin records the number of
voxels in the original dataset which had a combination of
, but we
want to do more than measure their individual probability
distributions. We are interested in the probabilities associated with
the relationship between the three variables. The most
straight-forward way to do this is with a three dimensional histogram,
with one axis for each of the variables. The span of each axis
represents a fixed range of values for the corresponding variable.
Each axis is divided into some number of (one dimensional) bins,
causing the interior volume is to be divided into a three dimensional
array of rectilinear bins, not unlike the voxels of a standard
volumetric dataset. Each bin in the three dimensional histogram
represents the combination of a small range of values in each of the
three variables. The value stored in each bin records the number of
voxels in the original dataset which had a combination of ![]() ,
, ![]() ,
and
,
and ![]() values covered by that bin. This
structure is termed the ``histogram volume'', seen in
Figure 4.1.
values covered by that bin. This
structure is termed the ``histogram volume'', seen in
Figure 4.1.
 |